Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakayama, Masashi
JAEA-Review 2023-032, 159 Pages, 2024/02
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of relevant technologies for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste through investigating the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary rocks at Horonobe Town in Hokkaido, north Japan. In the fiscal year 2022, we continued R&D on "Study on near-field system performance in geological environment", "Demonstration of repository design options", and "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations". These are identified as key R&D on challenges to be tackled in the Horonobe underground research plan for the fiscal year 2020 onwards. Specifically, "full-scale engineered barrier system (EBS) performance experiment" and "solute transport experiment with model testing" were carried out as part of "Study on near- field system performance in geological environment". "Demonstration of engineering feasibility of repository technology" and "evaluation of EBS behaviour over 100 C" were addressed for "Demonstration of repository design options". A study on "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations" was also implemented in two areas, "evaluation of intrinsic buffering against endogenic and exogenic processes" and "development of techniques for evaluating excavation damaged zone (EDZ) self-sealing behaviour after backfilling". The Horonobe International Project (HIP) was initiated in February 2023 to promote research and development in collaboration with national and international organizations.
C" were addressed for "Demonstration of repository design options". A study on "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations" was also implemented in two areas, "evaluation of intrinsic buffering against endogenic and exogenic processes" and "development of techniques for evaluating excavation damaged zone (EDZ) self-sealing behaviour after backfilling". The Horonobe International Project (HIP) was initiated in February 2023 to promote research and development in collaboration with national and international organizations.
Mohamad, A. B.; Udagawa, Yutaka
Nuclear Technology, 210(2), p.245 - 260, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:68.31(Nuclear Science & Technology) structure transition under high pressure
structure transition under high pressureYamanaka, Takamitsu*; Nakamoto, Yuki*; Sakata, Masafumi*; Shimizu, Katsuya*; Hattori, Takanori
Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 51(1), p.4_1 - 4_10, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.16(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Neutron and synchrotron X-ray diffraction and electric conductivity measurements of FeTiO ilmenite were performed under pressures. Ilmenite structure is retained up to 28 GPa. Structure analysis revealed that FeO
ilmenite were performed under pressures. Ilmenite structure is retained up to 28 GPa. Structure analysis revealed that FeO and TiO
and TiO are compressible and less compressible below 8 GPa, respectively. The resistivity is lowest along the Fe-Ti direction that has shortest interatomic distance among all the metal ion pairs. The resistivity in the direction normal to c-axis monotonically decreases with pressure, whereas that along c-axis shows hallow-shape with pressure. Maximum entropy analysis shows that electron configuration of Fe
are compressible and less compressible below 8 GPa, respectively. The resistivity is lowest along the Fe-Ti direction that has shortest interatomic distance among all the metal ion pairs. The resistivity in the direction normal to c-axis monotonically decreases with pressure, whereas that along c-axis shows hallow-shape with pressure. Maximum entropy analysis shows that electron configuration of Fe (3
(3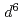 ) is more strongly changed than Ti
) is more strongly changed than Ti (3
(3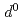 ) under compression. The anisotropic electrical conductivity and non-uniform structure change of Fe-Ti interatomic distance can be explained by the possible spin transition from high-spin state to intermediate-spin state of Fe cation.
) under compression. The anisotropic electrical conductivity and non-uniform structure change of Fe-Ti interatomic distance can be explained by the possible spin transition from high-spin state to intermediate-spin state of Fe cation.
Okitsu, Takayuki*; Hojo, Tomohiko*; Morooka, Satoshi; Miyamoto, Goro*
Tetsu To Hagane, 110(3), p.260 - 267, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0Taniguchi, Yoshinori; Mihara, Takeshi; Kakiuchi, Kazuo; Udagawa, Yutaka
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 195, p.110144_1 - 110144_11, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology) neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionZhou, Y.*; Song, W.*; Zhang, F.*; Wu, Y.*; Lei, Z.*; Jiao, M.*; Zhang, X.*; Dong, J.*; Zhang, Y.*; Yang, M.*; et al.
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 971, p.172635_1 - 172635_7, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Physical)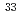 S-nuclear magnetic resonance measurements
S-nuclear magnetic resonance measurementsYoshida, Shogo*; Haga, Yoshinori; Fujii, Takuto*; Nakai, Yusuke*; Mito, Takeshi*; 8 of others*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(1), p.013702_1 - 013702_5, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Hirota, Noriaki; Nakano, Hiroko; Fujita, Yoshitaka; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Demura, Masahiko*; Kobayashi, Yoshinao*
The IV International Scientific Forum "Nuclear Science and Technologies"; AIP Conference Proceedings 3020, p.030007_1 - 030007_6, 2024/01
Dynamic strain aging (DSA) and intergranular stress corrosion cracking (intragranular SCC) occur in high temperature pressurized water simulating a boiling water reactor environment due to changes in dissolved oxygen (DO) content, respectively. In order to clearly understand the difference between these phenomena, the mechanism of their occurrence was summarized. As a result, it was found that DSA due to intragranular cracking occurred in SUS304 stainless steel at low DO  1 ppb, while DSA was suppressed at DO 100 to 8500 ppb due to the formation of oxide films on the surface. On the other hand, when DO was increased to 20000 ppb, the film was peeled from the matrix, O element diffused to the grain boundary of the matrix, resulting in intergranular SCC. These results are indicated that the optimum DO concentration must be adjusted to suppress crack initiation due to DSA and intergranular SCC.
1 ppb, while DSA was suppressed at DO 100 to 8500 ppb due to the formation of oxide films on the surface. On the other hand, when DO was increased to 20000 ppb, the film was peeled from the matrix, O element diffused to the grain boundary of the matrix, resulting in intergranular SCC. These results are indicated that the optimum DO concentration must be adjusted to suppress crack initiation due to DSA and intergranular SCC.
Kato, Tomoaki; Yamagishi, Isao
JAEA-Technology 2023-018, 53 Pages, 2023/11
In the decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, radioactive carbonate slurry waste was generated using the Advanced Liquid Processing System (ALPS) pretreatment and temporarily stored in a high integrity container (HIC). In 2015, overflow of supernatant from HIC estimate as bubble retention in the carbonate slurry was discovered, increasing the need for a safety assessment of the carbonate slurry stored the HIC (HIC slurry). In this study, a carbonate slurry (simulated slurry) was prepared according to the Mg/Ca mass ratio in the ALPS inlet water of the HIC slurry which overflew the HIC. The effects of reaction time during the pretreatment process, suspended solids concentration (SS concentration), and settling time on the particle composition, morphology and rheological properties of the slurry were investigated. Evaluating the effect of reaction time and concentration process on chemical properties in slurry production, the effect of the reaction time was not confirmed in the simulated slurry that had undergone the concentration process, and slurry prepared at SS concentration of 150 g/L was composed of formless particles have a particle diameter of 0.4  m or less. We also investigate the effect of SS concentration on sedimentability, decrease in SS concentration by dilution with processing solution contributed to an increase in the initial slurry settling velocity. Furthermore, two different flow characteristics were observed depending on the settling time, suggesting that the slurry at the initial settling time has non-Bingham flow properties, whereas it changes to Bingham flow properties as the settling time becomes longer. In addition, yield stress was increased with settling time, and this yield stress was found to be exponentially proportional to the density of the slurry. These results provide knowledge to estimate the current state of HIC slurry and are expected to contribute to the safety assessment.
m or less. We also investigate the effect of SS concentration on sedimentability, decrease in SS concentration by dilution with processing solution contributed to an increase in the initial slurry settling velocity. Furthermore, two different flow characteristics were observed depending on the settling time, suggesting that the slurry at the initial settling time has non-Bingham flow properties, whereas it changes to Bingham flow properties as the settling time becomes longer. In addition, yield stress was increased with settling time, and this yield stress was found to be exponentially proportional to the density of the slurry. These results provide knowledge to estimate the current state of HIC slurry and are expected to contribute to the safety assessment.
Nakayama, Masashi
JAEA-Review 2023-019, 70 Pages, 2023/11
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of relevant technologies for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste through investigating the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary rocks at Horonobe Town in Hokkaido, north Japan. In the fiscal year 2023, we continue R&D on "Study on near-field system performance in geological environment", "Demonstration of repository design options", and "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rocks to natural perturbations". These are identified as key R&D challenges to be tackled in the Horonobe underground research plan for the fiscal year 2020 onwards. In the "Study on near-field system performance in geological environment", we conduct the coupled analysis on the full-scale engineered barrier system performance experiment and test the coupled simulation code through comparison with different simulation codes in the international DECOVALEX-2023 collaboration project. Borehole investigations are also carried out for solute transport experiments in the Koetoi Formation. As for "Demonstration of repository design concept", we carry out in situ experiments and data analysis on concrete deterioration under the subsurface conditions. Geophysical surveys are also carried out around an experimental tunnel to be newly excavated at the 350m gallery and characterise the initial conditions of the excavation damaged zone. For the "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rocks to natural perturbations", we analyse the results of the hydraulic disturbance tests conducted in previous years and understand the relationship between rock stress / stress state and fault / fracture hydraulic connectivity. Concerning the construction and maintenance of the subsurface facilities, the 350 m gallery is extended and shafts are sank to a depth of 500 m.
 C
CMohamad, A. B.; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Furumoto, Kenichiro*; Okada, Yuji*; Sato, Daiki*
Corrosion Science, 224, p.111540_1 - 111540_15, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Ozu, Akira; Toh, Yosuke
Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 55(11), p.4002 - 4018, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Fukahori, Tokio
INDC(JPN)-210 (Internet), 5 Pages, 2023/10
The  U(n,f) cross section values were not correctly compiled in the ENDF format, and wrong values are disseminated in the JENDL/HE-2007 file. The high energy part of the
U(n,f) cross section values were not correctly compiled in the ENDF format, and wrong values are disseminated in the JENDL/HE-2007 file. The high energy part of the  U(n,f) cross section for the JENDL/HE-2007 library was evaluated by using the results of the FISCAL code. The correct
U(n,f) cross section for the JENDL/HE-2007 library was evaluated by using the results of the FISCAL code. The correct  U(n,f) cross section values of the JENDL/HE-2007 library above 200 MeV is given in this report.
U(n,f) cross section values of the JENDL/HE-2007 library above 200 MeV is given in this report.
Kamide, Hideki; Kawasaki, Nobuchika; Hayafune, Hiroki; Kubo, Shigenobu; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Maeda, Seiichiro; Sagayama, Yutaka; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Sumita, Junya; Shibata, Taiju; et al.
Jisedai Genshiro Ga Hiraku Atarashii Shijo; NSA/Commentaries, No.28, p.14 - 36, 2023/10
Developments of next generation nuclear reactors, e.g., Fast Reactor, and High Temperature Gas cooled Reactor, are in progress. They can contribute to markets of electricity and industrial heat utilization in the world including Japan. Here, current status of reactor developments in Japan and also situation in the world are summarized, especially for activities of Generation IV International Forum (GIF), developments of Fast Reactor and High Temperature Gas cooled Reactor in Japan, and SMR movements in the world.
Miura, Takatomo; Kudo, Atsunari; Koyama, Daisuke; Obu, Tomoyuki; Samoto, Hirotaka
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/10
Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP) had reprocessed 1,140 tons of spent fuel discharged from commercial reactors (BWR, PWR) and Advanced Thermal Reactor "Fugen" from 1977 to 2007. TRP had entered decommissioning stage in 2018. In order to reduce the risk of High Active Liquid Waste (HALW) held at the facility, the vitrification of HALW is given top priority. HALW generated from reprocessing of spent fuel contains not only fission products (FPs) but also trace amounts of uranium (U) and plutonium (Pu) within the liquid and insoluble residues (sludge). Under normal conditions, concentrations of U and Pu in HALW are very low so that it can not reach criticality. Since FPs with high neutron absorption effect coexists in HALW, even if the cooling function is lost due to serious accident and HALW evaporates to dryness, it is considered that criticality would not been reached. In order to confirm this estimation quantitatively, criticality safety evaluations were carried out for the increase of U and Pu concentrations by evaporation of HALW to the point of dryness. In this evaluation, infinite multiplication factors were calculated for each of solution system and sludge system of HALW with respect to the concentration change through evaporation to dryness. It is confirmed it could not reach criticality. The abundance ratios of U, Pu and FPs were set conservatively based on analytical data and ORIGEN calculation results. Multiplation factors for two-layer infinite slab model of solution and sludge systems of HALW were also calculated, and it was confirmed it could not reached criticality. In conclusion, the result was gaind that there could be no criticality even in the process through evaporation to dryness of HALW in TRP.
Suzuki, Seiya; Nemoto, Yoshihiro*; Shiiki, Natsumi*; Nakayama, Yoshiko*; Takeguchi, Masaki*
Annalen der Physik, 535(9), p.2300122_1 - 2300122_12, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Yokoyama, Miki*; Onuma, Susumu*; Osawa, Hideaki; Otomo, Shoji*; Hirose, Yukio*
Humanities & Social Sciences Communications (Internet), 10(1), p.623_1 - 623_10, 2023/09
This study demonstrates that a decision-making process utilising "the veil of ignorance" concept, defined in process terms as beginning from a blank slate encompassing the entire country as potential sites and shortlisting candidate sites based on scientific (geological) safety, promotes public acceptance of siting a repository for the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste and fosters procedural fairness.
Narukawa, Takafumi; Hamaguchi, Shusuke*; Takata, Takashi*; Udagawa, Yutaka
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 411, p.112443_1 - 112443_12, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology) observation of deformation behavior in high entropy alloys using neutron diffraction
observation of deformation behavior in high entropy alloys using neutron diffractionHarjo, S.
Nihon Kessho Gakkai-Shi, 65(3), p.178 - 182, 2023/08
Minari, Eriko*; Kabasawa, Satsuki; Mihara, Morihiro; Makino, Hitoshi; Asano, Hidekazu*; Nakase, Masahiko*; Takeshita, Kenji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(7), p.793 - 803, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:50.96(Nuclear Science & Technology)